Visualizing the linearity of the Arithmetic Linearity
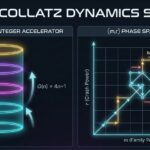
This interactive lab transforms the Collatz Conjecture from an abstract problem into a measurable physics experiment. This interactive lab visualizes the arithmetic stability of odd integers. . It “splits” an odd integer (N) into its two components—Floor(2n) and Ceil(2n+1)—and traces their trajectories side-by-side to detect where linearity breaks down.
It decomposes the integer by extracting the underlying parameter N and splitting the system into two distinct components:
- The Even Component: 2n
- The Odd Component: 2n+1, so that N = 2n + 2n+1 = 4n+1
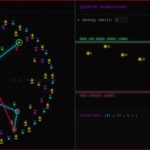
How to Read the Experiment:
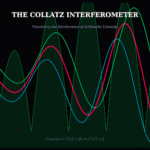
- The Beam Split: The Red Ribbon tracks the trajectory of the main integer (4n+1). The Cyan and Green ribbons track its decomposed parts (2n and 2n+1).
- The Linearity Check: As long as the sum of the components equals the whole (T(2n) + T(2n+1) = T(4n+1)), the system is linear.
- The Decoherence: When the ribbons drift apart and the Oscilloscope (Bottom) spikes, it reveals exactly where the arithmetic linearity breaks down due to parity mismatches.