1. Simulation Overview 🎯
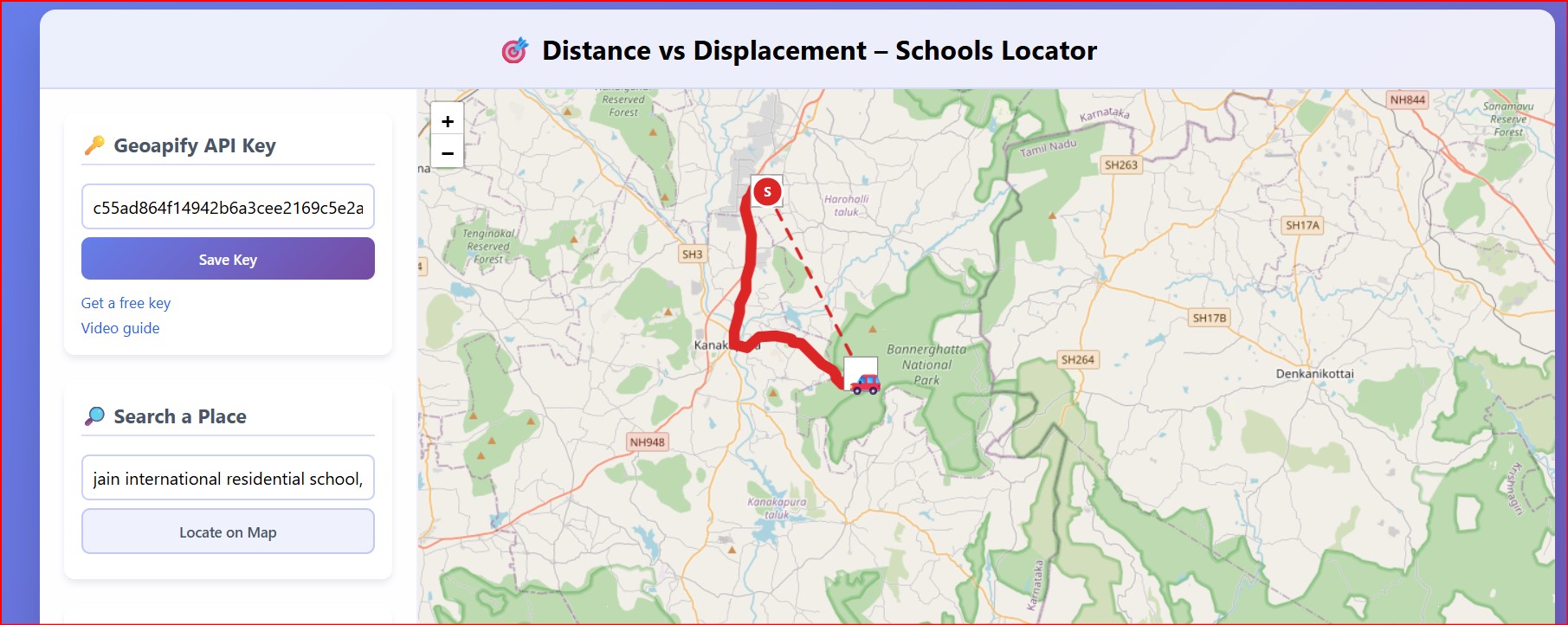
Concept: This app lets you plot a real-road route (distance) and the straight-line shortcut (displacement) between any two points on Earth.
Why it matters: Students often treat distance and displacement as synonyms; visualising both on an actual map makes it crystal-clear that distance ≥ displacement and that only vectors carry direction. This tool can be accessed at https://prayogashaala.com/wp-admin/simulations/distance3.html
2. How It Was Built 🛠️
a. Construction Methods (Step-by-Step) 🪜
-
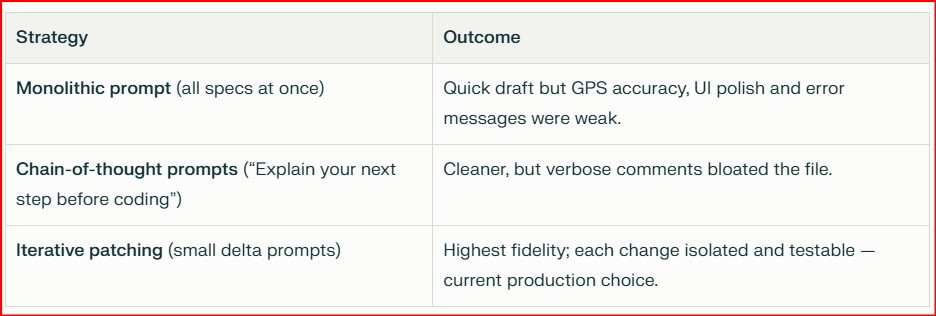
Prompt design – a detailed requirement list (see below) was fed to a generative-AI code assistant.
-
Skeleton generation – the model produced a single-page HTML file with Leaflet.js, CSS and vanilla JS.
-
Iterative refinement – successive prompts added GPS accuracy checks, map-click workflow, 🔑 input, a radius slider and a modal confirmation dialog.
-
Testing – routes were validated in Bangalore, Delhi and London to ensure the Haversine displacement matched Google Earth great-circle values.
-
User-configurable API key – internal key hard-coding was replaced by a “🔑 Geoapify API Key” panel that stores the key in
localStorage. A video showing how to obtain this API key step by step instructions is as shown below.
b. Prompt Used (Initial Seed) 💬
Create a complete web based physics simulation with the following specifications:
Core Functionality
Interactive map-based physics simulation demonstrating distance vs displacement concepts
…the route animation must last 5 seconds, show a thick 10 px line, include car/bike/walk speeds, calculate efficiency…
Technical Requirements
Leaflet.js only, Geoapify Places & Routing, responsive design, no external dependencies…
Educational Features
Haversine displacement, route efficiency, misconceptions, student worksheet…
3. Software & Tools 💻🔧
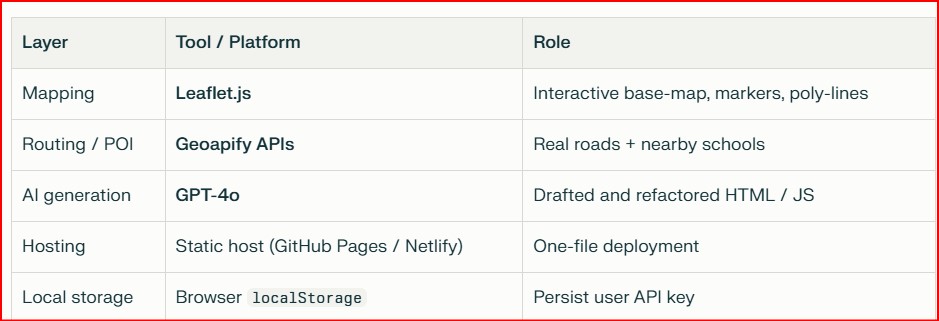
4. Logic & Frameworks 🧮
a. Underlying Logic 🧑🔬
-
Distance (d): sum of poly-line segment lengths returned by Geoapify route.
-
Displacement (Δr): direct great-circle arc via the Haversine formula.
-
Efficiency: η= (Δr/d ) x 100 %
-
Travel time: t=dvvehiclet=vvehicled with preset speeds (🚗 50 km h⁻¹, 🚴 20 km h⁻¹, 🚶 5 km h⁻¹).
A 5 s setInterval loop interpolates 110 waypoints so the icon glides smoothly along the path while a 10 px “snake” line grows behind it.
5. Prompting Frameworks 🧠✨
6. How to Use the Simulation 📚🕹️
a. User Guide ( Click here to Open the Simulation )
Paste your Geoapify API key in the
panel → Save.
Type a city or landmark → Locate on Map.
Click
Click on Map and tap the exact start point.
Adjust the radius slider (0 – 15 km).
Hit Find Nearby Schools → choose a school from the list.
Select a vehicle (
/
/
).
Press
Start Animation. Watch the icon travel the route while results update in real time.
b. Tips & Tricks 
Drag the start marker to fine-tune its position before searching.
Set radius to 0 km to test error handling when no POIs exist.
Compare efficiencies for walking vs driving in a dense city centre.
Worksheet Questions:
Why can efficiency exceed 90% in rural areas but fall below 30% downtown?
Design a looped route where displacement = 0 but distance > 0. What efficiency do you get?
Predict how efficiency changes if you double every poly-line waypoint.
7. What Makes It Unique 🌟
a. Comparison with Other Simulations

b. Educational Value 📖
-
Misconception spotlight: Students see why “shortest path” ≠ “shortest distance”.
-
Authentic context: Real roads anchor physics to everyday travel.
-
Prompt-engineering showcase: Changing a single instruction reshapes both code and pedagogy.
Whether you’re a student, educator, or curious explorer, this simulation is your gateway to hands-on, AI-enhanced learning. Dive in, experiment, and let the journey from physics to philosophy begin! 🎓🚀